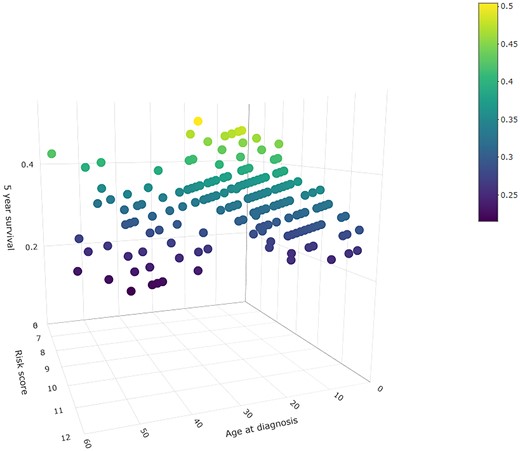
by Usha Govindarajulu | Apr 9, 2025 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
April 9, 2025 The authors have generalized the pseudo-observations approach to bivariate survival data subject to right censoring. Pseudo-observations approach was originally developed by Anderson (2003) for estimating covariates effect on time-to-event data. This...
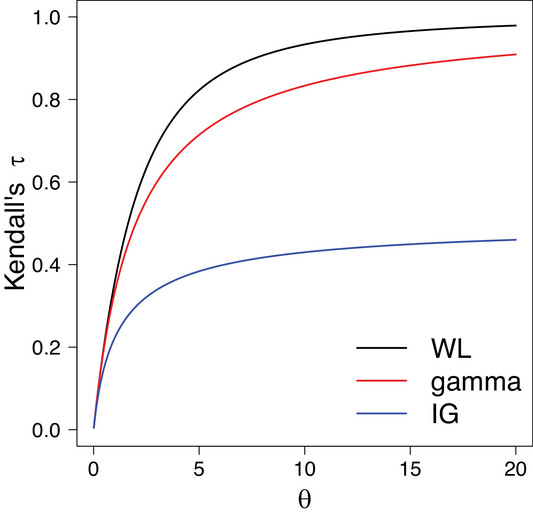
by Usha Govindarajulu | Mar 27, 2025 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
March 26, 2025 Their primary goal of their paper was to introduce a novel frailty model based on the weighted Lindley (WL) distribution for modeling clustered survival data. They used the weighted Lindley as the frailty distribution. This was a two parameter...
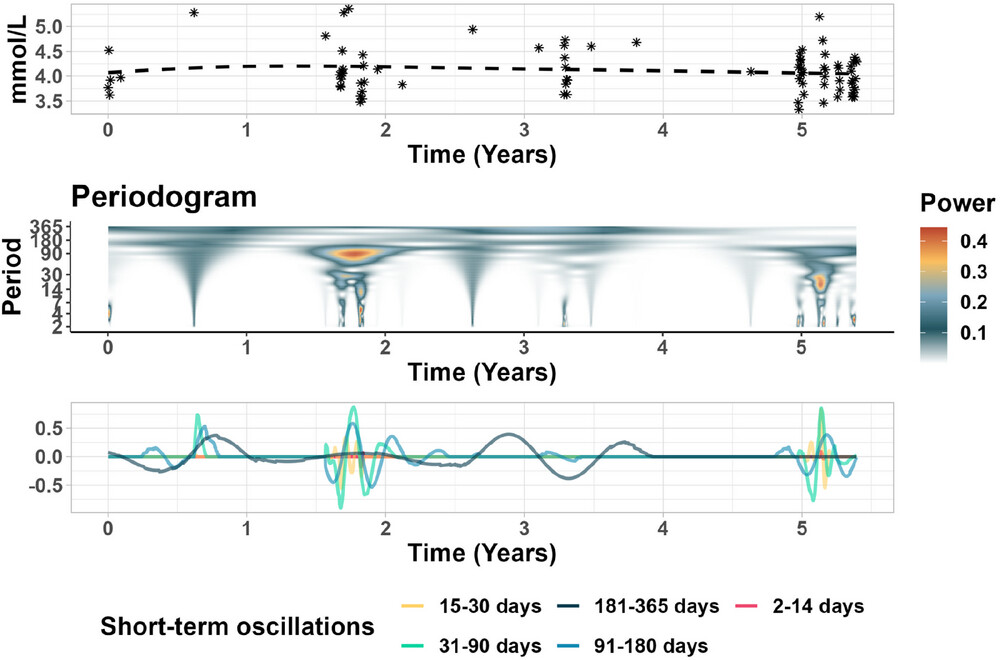
by Usha Govindarajulu | Mar 12, 2025 | Biostatistics, Blog, Healtcare
March 12, 2025 The authors used a novel method based on wavelet filtering and landmarking to obtain the prognostic role of a biomarker in patient death. Wavelet filters have been common in time series data to extract features and reduce noise. They also utilized...
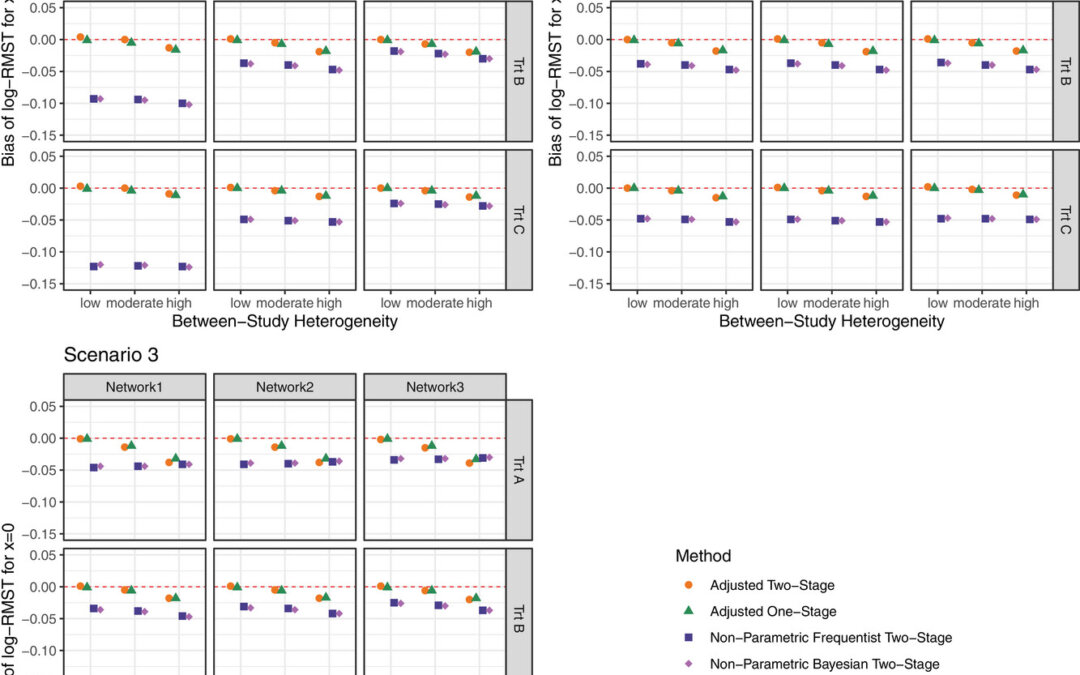
by Usha Govindarajulu | Feb 26, 2025 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
February 26, 2025 The authors have used network meta-analysis (NMA) to compare multiple treatments simultaneously using restricted mean survival time (RMST) with individual level data (IPD). Since the NMA was mainly used with aggregate data, they had to extend this...
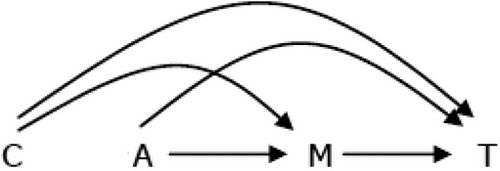
by Usha Govindarajulu | Feb 12, 2025 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
February 12, 2025 The authors focused on causal mediation analysis in survival analysis, more specifically with additive hazards modeling with an exposure by mediator interaction term. The causal mediation framework had come about over time from the mediation area and...
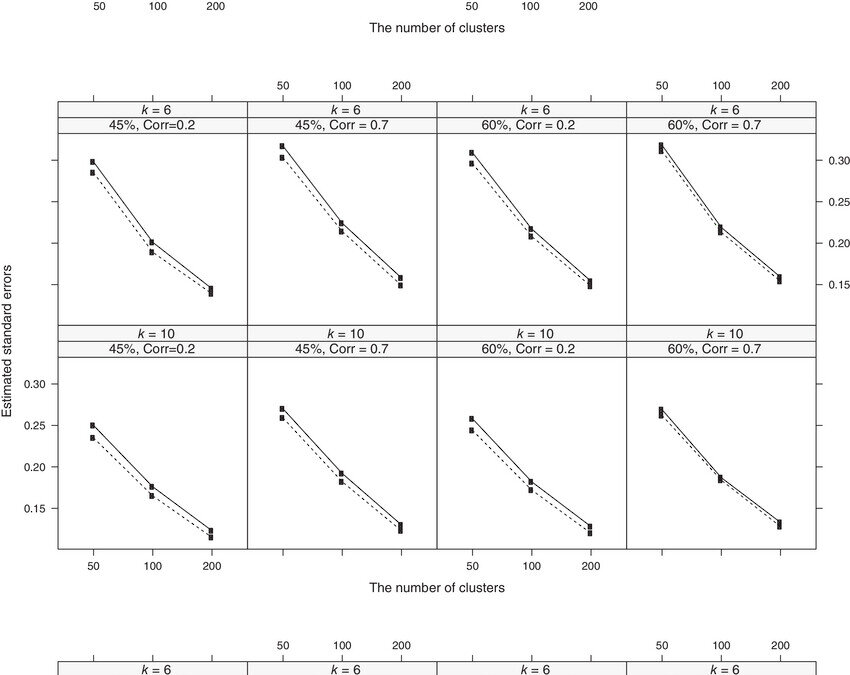
by Usha Govindarajulu | Jan 29, 2025 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
January 29, 2025 Many analyses have used clustered data but not everyone considers that clusters may be informative. For example, generalized estimating equations (GEE) and marginal proportional hazards model have been widely used to estimate population-average...






