by Usha Govindarajulu | Feb 25, 2026 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
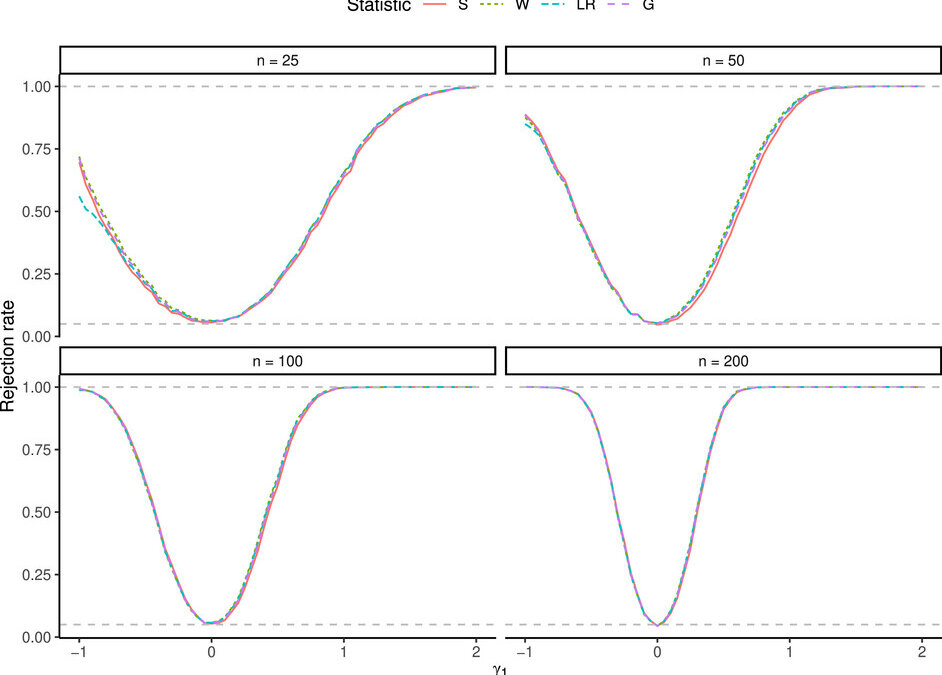
February 25, 2026 The authors explored new modeling for discrete paired data without normality assumptions. Skellam (1946) introduced the Skellam distribution as the difference of two Poisson random variables; Kozubowski and Inusah (2006) proposed the skew discrete...

by Usha Govindarajulu | Feb 11, 2026 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
February 11, 2026 The authors in this article have presented a stepwise guidance on how to extend the simple time-to-first event model to complex multistate methodology, where multiple events are incorporated. They considered non- and semiparametric methods and show...

by Usha Govindarajulu | Jan 30, 2026 | Biostatistics, Blog, Healtcare, Machine Learning, Professor, Usha Govindarajulu
January 28, 2026 Machine learning (ML) offers opportunities to overcome limitations of conventional survival analyses, which are commonly found in cancer studies. It becomes unclear whether they consistently outperform traditional statistical methods and whether one...
by Usha Govindarajulu | Jan 14, 2026 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
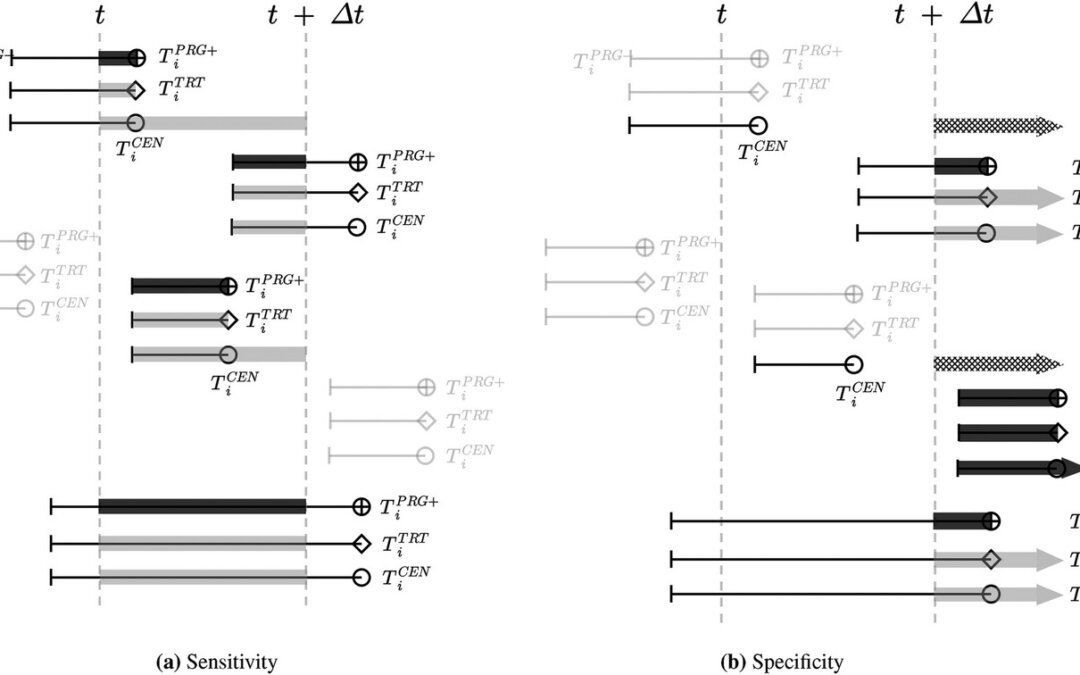
January 14, 2026 To evaluate the performance of a prediction model in time-to-event outcomes with censoring is very difficult. Interval censoring and competing risks present additional challenges. They proposed two methods to deal with interval censoring: a...
by Usha Govindarajulu | Dec 30, 2025 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
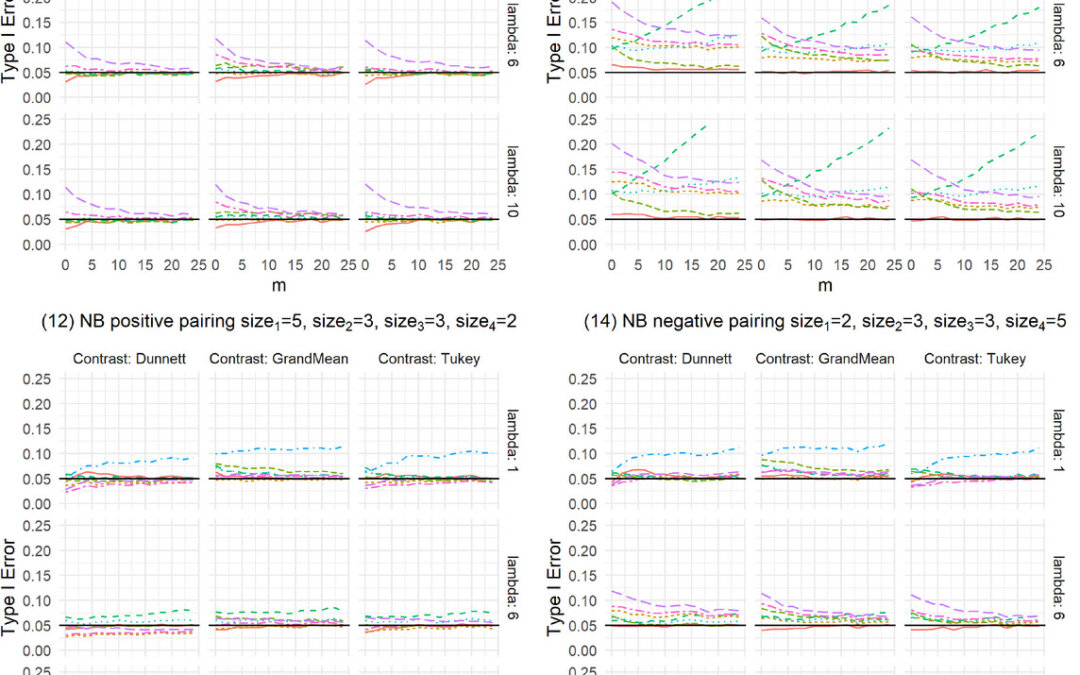
December 31, 2025 Count data are collected in many different types of experiments, yet their analysis remains challenging, especially in small sample sizes. Until now, linear or generalized linear models (GLMs) with either a Poisson or Negative Binomial distribution...
by Usha Govindarajulu | Dec 18, 2025 | Biostatistics, Blog, Usha Govindarajulu
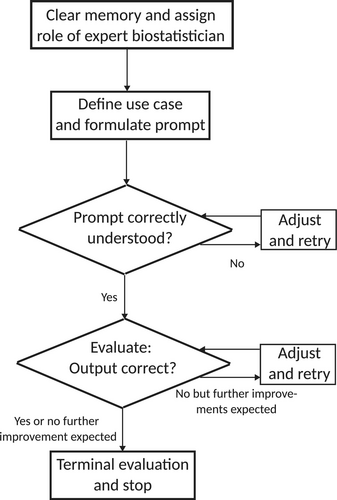
December 17, 2025 A previously published paper, ChatGPT as a Tool for Biostatisticians: A Tutorial on Applications, Opportunities, and Limitations by Dobler et al. that also appeared in Statistics in Medicine, which according to Zhu provides a timely and insightful...






